GUEST COLUMN: Timely action saves lives: first-correct response methods for critical diseases-Dr Puri
Dr Ajit S Puri/ royalpatiala.in News/ January 17,2026
Emergency medical treatment is of paramount importance and needs to be carried out in cases of emergencies, contingencies and crises.
The guidelines, given below, regarding the emergencies of various serious diseases, though not exhaustive, will be highly useful in most of the cases. If applied properly and seriously, a life may be saved, or at least further deterioration of the patient may be altogether stopped, till he/ she gets proper medical aid.
- HEART ATTACK
Any pain-killer, especially an injection like norphin/ tidigesic or the like, should be administered immediately. These medicines are also available in the form of tablets. There is no harm caused by these drugs even if later investigations do not reveal a heart problem. Half a tablet of Disprin is also valuable in such cases. A tablet of glyceryl trinitrate may be kept under the tongue of the patient with the advice of the physician. The patient should be shifted to hospital immediately.
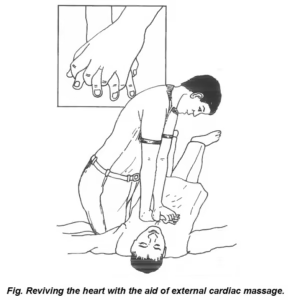
Reviving the heart
At times the heart attack is so severe that the heartbeat stops immediately, and it may occur so unexpectedly as to warrant instant personal attention, which is not available. Reviving the heart is very rewarding, provided the technique is known. In such a situation, even an unknown person can help a dying patient, because the heart has to be revived within 3-4 minutes after the collapse of the patient. Afterwards, it may not prove to be of any value. Hence, the technique should be known to almost everybody or to as many people as possible.
Technique for reviving the heart
In such a situation, the heart is revived by an ‘external cardiac massage’. The patient is made to lie on the floor with the back touching the ground. Without losing time, the neck of the patient is pulled backward and his legs raised. The legs are kept elevated till the procedure is over. No pillow or anything else is required to be kept under the head. One person places his palm on the lower part of the sternum (i.e. the bone located in front of the centre of the chest), and immediately puts the other palm upon the palm already placed on the sternum, and keeps the fingers extended or interlocked, as shown in Figure. Now, with the help of the two palms, the sternum bone is pressed 80 times a minute, and this pressure should not be more than 4-5 cm. To avoid fatigue, the best course is for the person to kneel against the side of the patient, bending over his chest. He should keep both his arms straight while putting his palms on the chest for the massage / pressure.
If some other person is available, he should start mouth-to-mouth breathing. In this process, he forces his expiration into the mouth of the patient. During this time, the nose of the patient should be closed, otherwise the air forced into the mouth of the patient will come out through the nose. One breath after every five times of the cardiac massage is required. If no other person is available, two breaths should be given after every 15 times of the cardiac massage, by the same person doing cardiac massage.
- DIABETIC COMA
Needs specialist treatment in a hospital.
- EPILEPSY
Marked convulsions may be observed in a patient of epilepsy at odd hours / place. The attacks may come one after another. In such a situation, an injection of lorazepam, slowly and intravenously, is highly useful, and the attack is likely to subside instantaneously, especially in mild to moderate cases. Since the patient will be almost unconscious, it should be ensured that his neck is straight. At the same time it should be seen that the patient does not bite his tongue. This can be prevented by placing the handle of a spoon wrapped in a cloth between the back teeth of the patient. Shifting the patient to hospital should be done after first aid has been administered.
- INJURY TO THE HEAD, SPINE, CHEST, ABDOMEN, FRACTURES AND BURN INJURIES
Injury to the head, spine, chest and abdomen requires immediate attention. The injury may cause a wound, or it may be a blunt one, both are equally serious. There may be a fracture of the skull, or of the ribs, or of the spine.

If there is a wound, emergency measures should immediately be adopted before the patient is taken to the hospital. A sharp wound usually bleeds profusely. Clean the wound, cut the surrounding hair, apply any antiseptic lotion and quickly put the pressure bandage. An injection of tetanus toxoid should be given for the prophylaxis of tetanus.
HEAD INJURY
Injury to the head, however minor, must be attended to, as in some of the cases, symptoms of the head injury start appearing after 48-72 hours, and in some even later. The reason is that following the head injury, a small amount of blood goes on collecting in the brain, and when a sufficient amount of blood collects in the brain, say in about one, two or three days, the symptoms become apparent. In view of this, the dictum is that the patient of a head injury must be kept under observation in a hospital, even though the injury may be minor and the patient feels normal. A computed tomographic (CT) scanning of the head must be taken to rule out any pathology in the skull or brain.
SPINAL INJURIES
These are mostly either accidental or due to fall from a height. Such cases need urgent attention in specialized injuries centers. Creation of trauma centers on highways helps in starting the treatment in no time in accidental cases.
INJURY TO CHEST AND ABDOMEN
In all cases of chest injuries, chest X-rays must be taken and urgent treatment should be given in a hospital, if there is any fracture of the ribs and / or injury to the lungs.

However, cases of injuries to the abdomen require very careful attention. If the intestines have come out, put sterilized gauze or cotton over the protruded viscera and apply loose bandage across the abdomen. Outside the operation theatre, never try to force the viscera into the abdominal cavity as an emergency measure.
BURN INJURIES
Mass awareness about burns injuries is very important. Adults/ elderly should keep in mind that children are likely to get burn injuries from bursting crackers during festivals or special occasions. In case accident does occur, pour water on the burnt area of the skin for at least 15-20 minutes depending upon the severity of the burn. With this measure, raised temperature of the burnt area shall be lowered and cells of the skin shall be saved from dying as a result of heat. Cover the burnt area with a clean cloth/ towel, as burnt injuries are usually sterile in the beginning. Antiseptic ointments can be applied including the administration of antibiotics and pain-killers etc. In severe cases, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital.
FRACTURES
Fractures may be simple, where there is no wound or compound, which are accompanied by wound /wounds. Sometimes there may be even multiple fractures. In case there is a wound, it should be treated. In case there is profuse bleeding, a string/tourniquet should be tied on the limb above the bleeding area, so that the patient may not die due to profuse bleeding and shock. A pain-killer injection, whichever is available, should be given promptly, if possible. The tourniquet must be released every half an hour, so that circulation in the part of the limb below the tourniquet may not suffer. The patient should be rushed to hospital after giving immediate support to the fractured area, as described below:
In the case of the fracture of the upper arm (humerus), tie the upper arm to the trunk with a piece of cloth or bandage. Do not forget to keep the other arm free, and the best would be to ask the patient to place the hand of the unaffected side over his head, before tying the fractured arm to the trunk. Use a sling for the fractured arm. For the fracture of the forearm, apply wooden splints (after applying cotton and bandage over these splints) over the two surfaces (anterior and posterior) of the forearm, and then tie with the help of bandage. A sling, of course, will have to be used. For any fracture of the lower limb, tie the fractured limb to the normal limb. For example, if there is a fracture of the femur (thigh), tie the fractured thigh to the other thigh with the help of any bandage, and so on.
Remember that whenever any injury or fracture occurs, the patient should not be given anything to eat or drink, since some sort of immediate operation may be required on reaching the hospital, which may not be possible if the patient has a full stomach. The reason is that administering general anaesthesia, which may be required, will not then be possible immediately.

Dr. VJS Vohra says: “Serving in the field of Disability Empowerment for over 52 years, Dr. VJS Vohra, CEO and Senior Consultant of Nevedac Prosthetic Clinic, Chandigarh has been carrying forward the legacy of his father, Padmashri Col. D.S. Vohra. Dr Vohra’s life mission is to restore mobility by providing artificial limbs and orthotic supports, to empower the persons with disabilities, including large number of persons who are involved in road accidents, resulting in amputations and other disabilities.
The International Day of Persons with Disabilities, observed every year on 3rd December, and Road Safety activities in January are deeply significant occasions that reinforces the importance of promoting the rights, dignity, and well-being of persons with disabilities at every level of society. Taking into consideration the large number of road accidents in India, Dr. Vohra says road safety commitment or Disability Day should not be confined to one or a few days only, but every day of the year must be a commitment to uphold the safety of persons on the road travelling by any mode transport, including pedestrians.”
To conclude, it should be stressed that the only way to prevent immediate as well as late/serious complications of fatal diseases/accidental cases is that mass awareness should be created for learning and practising various first-aid measures, so that the life of the affected/injured person can be saved.
Introduction of post graduation courses like M.D. in emergency medicine (already available in selected developed countries) would help in dealing with all sorts of emergencies more effectively.

Undoubtedly, this is the need of the hour, considering the fast-increasing incidence of mortalities in such situations.
Roads are for journey, not for racing.
The best drivers are aware that they must be aware.
Safe travels, no matter the distance.
Leave sooner, drive slower, live longer.
Follow traffic rules, save your future.
NOTE: The views expressed by the author/ writer are personal.